Knowing the Different Germs: Bacteria Vs Viruses
When we look at kitchen sanitisers, antibacterial cleaners, and disinfectants, we look at their kill rate 99.9 or 99.999% and do they kill E.coli, Salmonella, Staphylococcus, Pseudomonas, Influenza, H1N1 Bird Flu and Norovirus. However, it's also important to know what these bugs are and what they do.

Bacteria
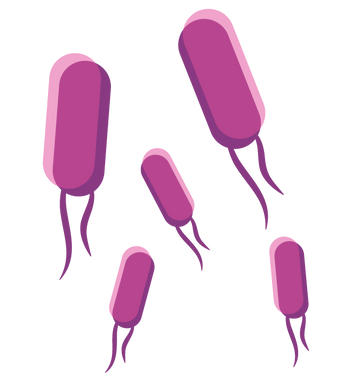
Bacteria is a simple single-cell organism that's only visible by microscope. Depending on its genetic material it can be spherical or rod-shaped and when multiplying, will grow in rows, uniform or non-uniform groups. We need bacteria (microflora) to aid digestion and produce vitamins such as K. Microflora in a healthy person shouldn't cause any issue and prevents infection, in a vulnerable person (child, elderly) it's more of a balancing act.
What are the most common infectious bacteria? How are they transferred and what types of illness do they cause?

E.coli
A rod-shaped like a piece of long-grain rice. Generally, it isn't harmful - happily residing in the lower gut, however, some strains are a problem. This food-borne disease causes severe gastroenteritis, fever and kidney damage, particularly vulnerable are children and the elderly. It does this by releasing toxins once it has died.
Found in meat products, E. coli gets into the food chain by poor hygiene management, allowing faecal matter to contaminate the raw meat. Prevention is the best way to tackle this bacteria, thorough cooking of meat, good hygiene practices that include the use of a bactericidal with a kill rate of 99.999% (EN1276) and hand washing.
Salmonella
Like E. coli, Salmonella is rod-shaped, and it causes gastroenteritis in the same way, with incubation periods being 12-36 hours.
Found in dairy products such as milk, eggs, raw chicken and some processed foods, Salmonella is the second most common type of food poisoning occurring in the UK. Wide-ranging, Salmonella can have a long life and is hard to eradicate. Excellent food handling that prevents cross-contamination and hand hygiene is essential.
Viruses
Viruses are a piece of genetic material within a protein coating. They have different structures and functions compared to other micro-organisms. They function as a parasite, infecting a host cell to replicate in the thousands. With a short lifespan outside of a host, viruses use food and surfaces as transport and a route to ingestion.

Hepatitis A
With a long incubation period and a low mortality rate, it is easy to overlook how severe Hepatitis A is. Contracted through poor personal hygiene when handling foods, it can also be ingested by drinking contaminated water or ice. Hepatitis A is highly infectious and damages the liver causing jaundice which affects the skin and eyes.
Other symptoms of Hepatitis A might include; fever, weakness and fatigue, joint pain and a reduced appetite. In some cases the patient may experience severe itching.
Influenza
Infection takes place through water droplets, mainly from coughing and sneezing or touching contaminated surfaces. Infection occurs when hands come into contact with eyes, nose and mouth. Influenza has a short incubation period of 48 hours from infection to illness.
Unlike a common cold, the sudden onset of symptoms may include high fever, coughing, sneezing severe muscle aches, chills and nausea. Regular hand washing/sanitizing, self-isolation and good hygiene will help prevent spread.
Norovirus
Known as the 'Winter Vomiting Bug', it's contracted by touching contaminated surfaces, eating foods prepared by infected people or being in close contact with someone carrying the virus itself. Symptoms normally present themselves within 1-2 days of being infected, and normally last around 2 days.
Norovirus causes intense discomfort through gastroenteritis, vomiting and diarrhoea - a passing virus with no long term effects. Regular hand washing, avoidance of alcohol gels and self-isolation should prevent spread.
Covid-19
Coronaviruses affect mammals and birds, and transfers between species. Symptoms present as respiratory tract infections (i.e. cold, flu-like, possible bronchitis and pneumonia type symptoms). Covid-19's outer layer is spiked to help anchor itself to a host cell so that it can infect the host more easily.
Its transferred by water droplets created by talking, coughing and sneezing. Droplets can be airborne for 10 minutes. Once they drop to the floor or a surface they don't degrade, there is evidence they can survive for up to 72 hours.
When it comes to germs, vigilance is key, good personal hygiene, good housekeeping, and adhering to strict food handling procedures all help.
If you want to know the difference between 99.9% and 99.999% kill rate look at our infographic explaining it all.











